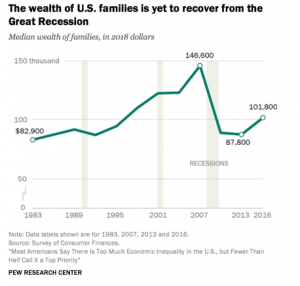
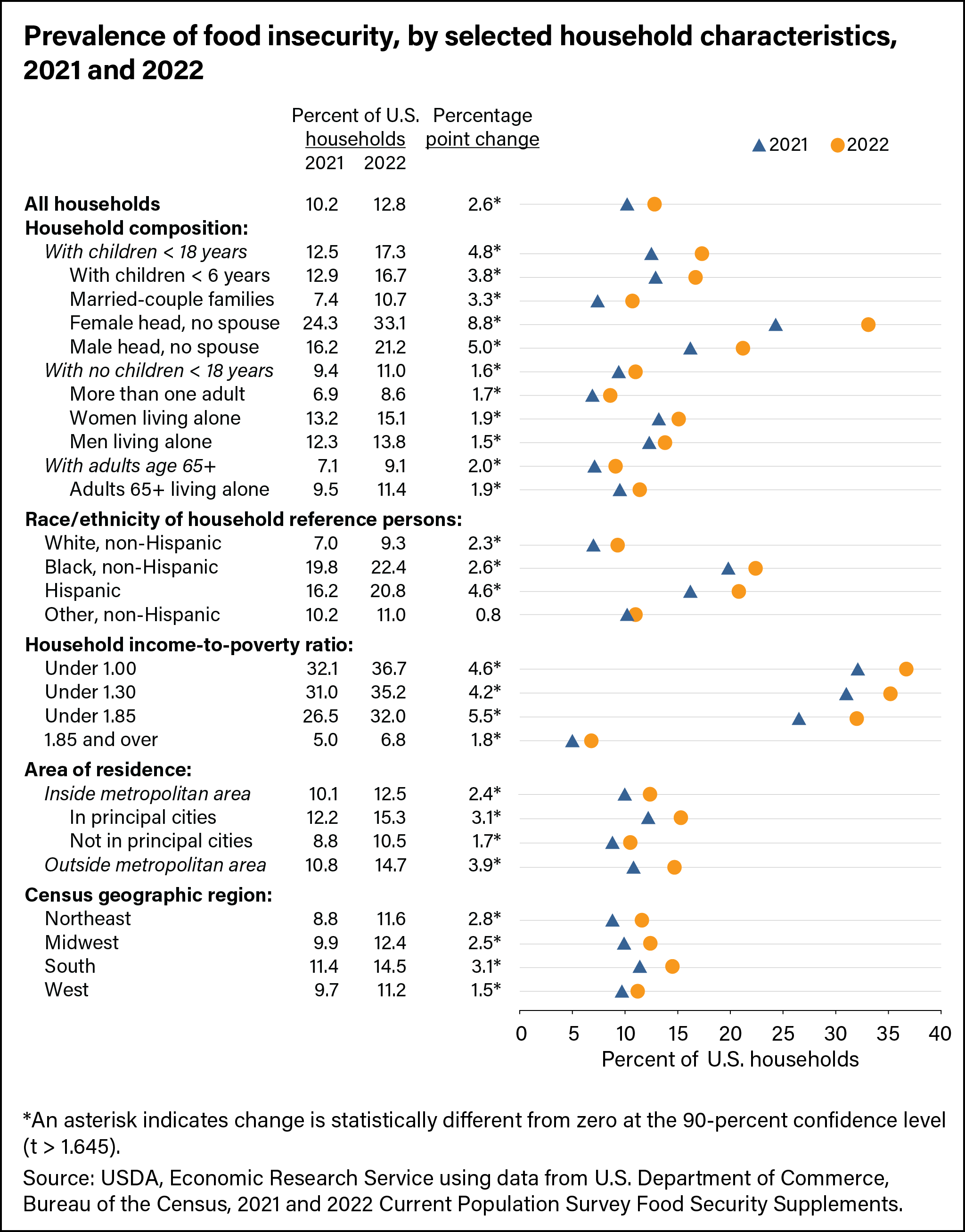
The issue of food insecurity is one that is very prevalent in the United States. Food insecurity, according to the USDA, can be defined in different ranges; either low food security or very low food insecurity. Low food security is when the quality or variety of one’s diet is undesirable, with not much, if any, reduced food intake. Very low food security is different from low food security in that reports of reduced food intake are made as well as the issues that are seen in low food security. Food is something that those who have never faced food insecurity often take for granted, however, for people who have faced it, it is a major issue, while affecting different groups of people in the United States disproportionately. As seen in the graph below, 10.5 percent of U.S. households in 2020 were food insecure and, of these households, 6.6% had low food security and 3.9% had very low food security.
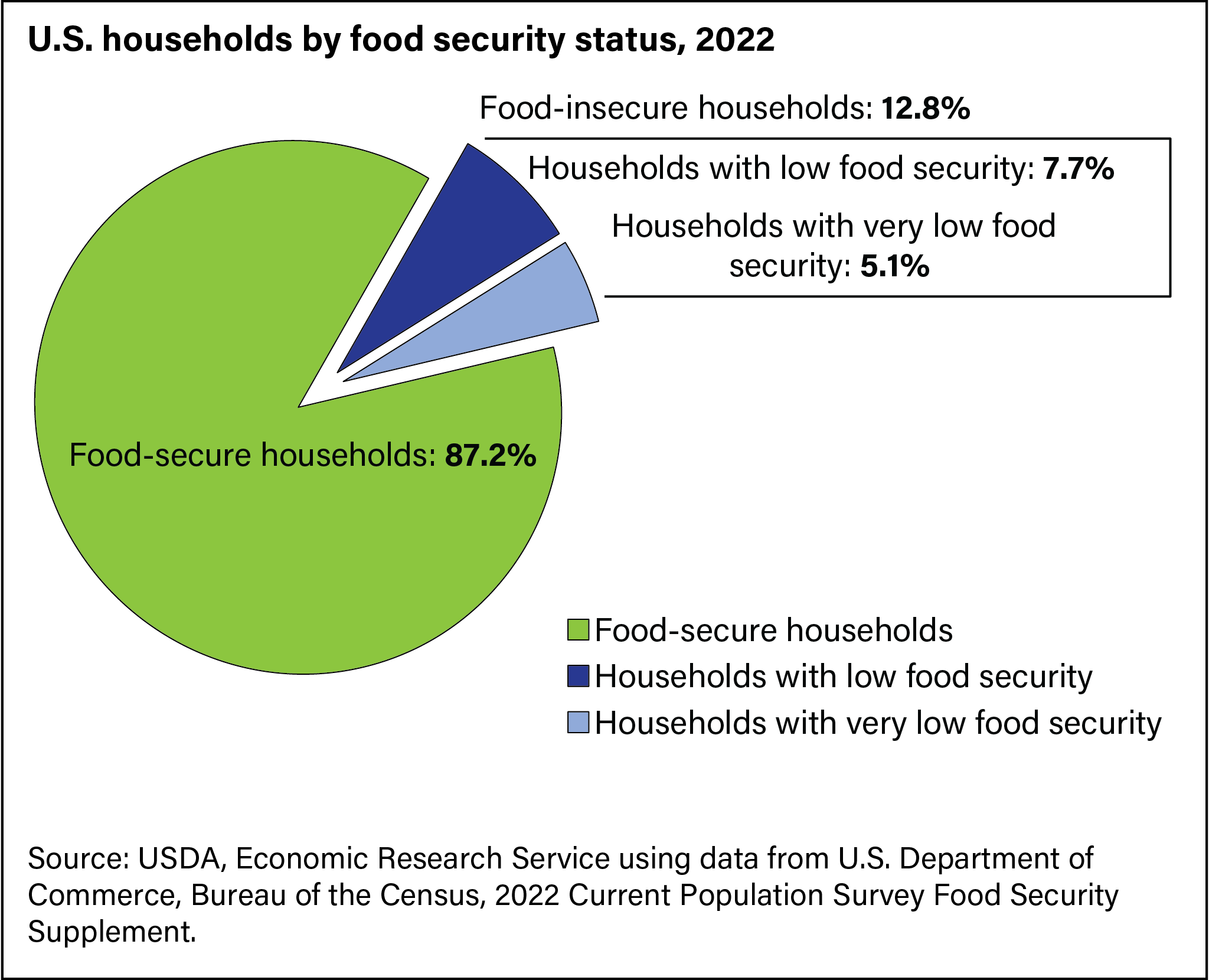
However, as I mentioned before, different households were more likely to have experienced food insecurity than others in the United States. For instance, as seen in the graph below, rates of food insecurity were much higher in Black (21.7%) and Hispanic (17.2%) households, showing how food insecurities disproportionately affect people of different races in the U.S. Households helmed by a single woman with children were also much more likely to become food insecure, with 27.7% of them being food insecure.
Nutrition is a major factor into one’s health and those who are food insecure are less likely to have the nutrition one needs to live happy, healthy lives. Until food insecurity for everyone is solved in the United States without the disparities in different groups as seen above, food security and insecurity will remain a major contributing factor to health problems for many in the U.S.