Sequence data was provided for all three of my isolates, however isolates 4 and 6 could not be identified. I was able to identify isolate number 11 though. I ran a sequence of 677 base pairs with BLAST. The closest match that came up was Klebsiella aerogenes (also known as Enterobacter aerogenes), with 98% identity and 10% query coverage (Accession number NR_102493.2).
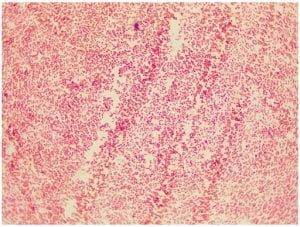
Klebsiella aerogenes is a very small, Gram negative rod. It is such a small rod, that is may sometimes appear to be a cocci at first glance. When I first looked at the Gram stain of isolate #11, I thought I was seeing cocci, however I was able to enlarge the image and what appear to be cocci, are actually very, very small rods (difficult to see in this image). Klebsiella bacteria tend to be rounder and thicker than other members of the Enterobacteriacecae family. The Gram negative pink color is consistent between my Gram stain and that of K. aerogenes.
Gram stain for isolate #11
Gram stain of Klebsiella aerogenes
Image: http://faculty.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/labmanua/lab12/Entaerogenes.html
Members of the Enterobacteriaceae family, Klebseilla are facultative anaerobic, nonmotile bacteria. The Klebsiella genus consists of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule (1). Klebsiella species can be found everywhere in nature, including in soil and water, on plants, and some strains are even considered to be a part of the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tracts of humans (1). One of the most well-known strains within this genus is K, pneumoniae, and ESKAPE pathogen, and a common pathogen of the human respiratory system that causes pneumonia (1). Some strains of Klebsiella have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by plants (2).
Image: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Klebsiella_pneumoniae
Image: http://microbe-canvas.com/Bacteria.php?p=422
Image: https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Klebsiella_pneumonia
There is little research that discusses the Klebsiella genus as antibiotic producers. In fact, the majority of the literature about this genus discusses how many species within the genus have become resistant to antibiotics, and produce beta-lactamases that have the ability to break down commonly used antibiotics (4). These are often referred to as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing bacteria (4). The most common ESBLs are E. coli and K. pneumoniae. In addition to ESBL production, there are certain Klebsiella strains that are cytotoxin producers, such as K. oxytoca (5). These strains of K. oxytoca have been implicated in antibiotic-associated hemorrhagic colitis. The clinical manifestations are usually preceded by antibiotic treatment with a Beta-lactam agent (5). Cytotoxins are chemical weapons that T-cells use to destroy infected cells, protecting healthy cells. Some cytotoxins works my making holes in the cell membrane, while others turn on a program that causes the cell to self destruct (5).
Sources:
- Parwanu, N., K. Rogers, and A. Tikkanen. 2010. Klebsiella Bacteria Genus. Encylopedia Britanica.
- Buckle, J. 2014. Learn more about Klebsiella. Science Direct.
- 2018. Klebsiella. Wikipedia Encylopedia.
- Provinvial Infection Control (PIC-NL). 2011. EXTENDED-SPECTRUM BETA-LACTAMASE (ESBL) PRODUCING BACTERIA. Health.gov.nl.ca
- Barson, W.J., and M.J. Marcon. 2012. Etiologic Agents of Infectious Disease. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 4th ed.